Features
Educating Children Affected By Insurgency
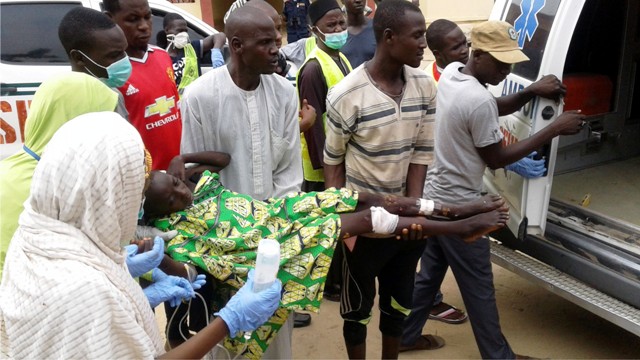
Education, be it formal or informal, is the foundation for the sound development of every child and one of the critical tools for the development of any society.
Every child has the right to education, which eventually empowers him or her to stand and become useful to the society, irrespective of race, religion and ethnicity.
In the light of its importance, educationists observe that inadequate education is one of the causes of armed conflicts, underdevelopment, agitations and evil in many nations.
They specifically identify poor education among the youth in the northern part of the country as a tool that insurgents use to perpetrate crisis by branding western education as evil which they translate to Boko Haram.
With this erroneous belief of the insurgents, they target education sector, setting schools on fire, killing and abducting students, in some cases.
The abduction of the 276 Chibok school girls on April 14, 2014, was an example of one of the group’s onslaught while it has also held many school girls and people hostage.
Worried by this development, a lawyer, Mr Zannah Mustapha, began to educate children in the region on the platform of his non-governmental organisation — Future Prowess Islamic Foundation School.
Founded in 2007 in Maiduguri with 36 persons to cater for orphans, widows and other victims of the insurgency, the school has graduated more than 1,000 and it has enrolled 626 in 2017 alone, most of who are girls.
According to Mustapha, the aim of the foundation is to stop insurgency by integrating children that are affected by insurgency and family members of Boko Haram in society through education.
He explained that inclusion of children and family members of Boko Haram insurgents in the foundation’s programme would prevent discrimination.
“The school provides free education, free meals uniforms and healthcare to children affected by violence.
“Those orphaned by the conflict on both sides, that is, the Boko Haram children and children of security operatives, are welcomed to the classroom as a sign of the reconciliation we hope to achieve for the region.
“Even a dog would not eat his own child and so, members of the Boko Haram insurgents would not want to attack a school where they know their own children and family members attend.
“The school has united them in love and they all see themselves as brothers and sisters, not minding who their parents are and with this, they would one day push for a stop to the violence,’’ Mustapha said.
According to him, the foundation’s method of including Boko Haram’s members will engage everybody to the mode of operation of the school in terms of dressing and subjects to be taught which all parties agreed to and signed as a document.
Mustapha commended the efforts and interventions of President Muhammadu Buhari in the fight against the insurgents with a note that without his efforts, negotiation with the insurgents would have been difficult.
He said the foundation had been able to function with the assistance of development partners such as the International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC), the Norwegian Refugees Council, United Nations High Commission for Refugees (UNHCR), the Borno Government and kind-hearted individuals.
He said while the ICRC had significantly relieved the school of the burden of expenditure on food through donations, Gov. Kashim Shettima of Borno paid the first three months’ salaries of teachers, among other assistance.
To ensure sustainable funding of the school, he said the foundation established a medium-scale fish pond and hatchery; ventures that had provided money support to the school activities.
However, Mustapha’s humanitarian work has not gone unnoticed as it has attracted the acknowledgement and recognition of the UNHCR and won him the 2017 Nansen Refugees Award.
The UNHCR recognised Mustapha’s brave works as one of the largest humanitarian emergency operations in between 2016 and 2017.
The commission notes that the intervention comes at a time when the country’s education sector is confronted by challenges of not getting thousands of youths enrolled in schools.
The UNHCR commended the award winner for his tenacity in operating the school not minding Boko Haram attacks on the education sector and the killing of teachers.
It also recognised Mustapha’s role in empowering women, his role in securing the release of the 82 Chibok school girls and negotiation for the release of hostages.
The United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees, Mr Filippo Grandi, described education as one of the most powerful tools for helping refugee children to overcome the horrors of violence and forced displacement.
“It empowers young people, equips them with skills and works to counter exploitation and recruitment by armed groups.
“Conflict can leave children with physical and emotional scars that are deep and lasting as it forces them from their homes, exposes them to unspeakable atrocities and often rips apart their families.
“The work Mustapha and his team are doing is of the utmost importance, helping to foster peaceful co-existence and rebuild communities in north eastern Nigeria; with this award, we honour his vision and services,’’ Grandi said.
Similarly, UNHCR Country Representative to Nigeria and the Economic Community of West Africa State (ECOWAS) Mr Jose-Antonio Canhandula, congratulated Mustapha as the first Nigerian Laureate of the Nansen Refugees award.
He commended Mustapha for using the school to promote peace and for his role in the negotiation for the release of the 82 Chibok School girls, setting up cooperatives for widows and providing empowerment programmes for nearly 600 women in Maiduguri.
Canhandula said it was for these extraordinary services that the committee chose him as winner of the 2017 Nansen Refugees Award among the five other nominees.
“Looking at Mustapha, the committee was strongly influenced by his dedication to abandoned and orphaned children, including children born by Boko Haram parents, who, in that environment, are rejected by society.
“He tries to bring all these children as well as orphans and widows and give them a sense of life, protection and livelihood, particularly through education and skills training for victims of the conflict.
“These are some of the criteria that the committee looked at and actually put him ahead of the five others from different continents.
“He represents a good platform and he is supposed to receive an award that includes some money for him to be able to continue; but money is not enough, particularly when you look at the kind of crises that we have in the North-East.
“UNHCR will support him to be able to sustain his works to generate more income for its own long-term sustainability.
“There are many rich and influential Nigerians we could reach out to and show them what he is doing and see how they can support him going forward in 2018,’’ Canhandula said.
On his part, the Secretary-General of the Norwegian Refugees Council, Mr Jan Egeland, noted that the recognition of Mustapha’s brave works pointed to the importance of education for the future of Nigeria.
UNHCR Nansen Refugees award was established in 1954 and awarded annually to an individual, group or organisation, in recognition of outstanding service to the cause of refugees, displaced and stateless persons.
The award includes a commonwealth medal and monetary prize of 100,000 dollars donated by the governments of Norway and Switzerland to begin a project in consultation with UNHCR.
The 2017 Nansen Refugees Award will be presented to Mustapha on October 2 in Geneva.
Okoji writes for News Agency of Nigeria.
Lizzy Okoji
Features
Vocational Education And Nigeria’s Economy
The importance of vocational training to the development of any nation cannot be over emphasised. Technical education experts define vocational education as any form of educational program or course that focuses on teaching the specific skills and knowledge required for a particular job or trade. Unlike traditional academic education, which is often broader and theoretical, vocational training is practical, hands-on, and tailored to prepare individuals for specific careers or industries. They also argue that the dearth of trained vocational and middle-level technical manpower represents a very serious gap in the development of third-world countries, including Nigeria. This argument, perhaps, underscores the Federal Government’s bold move towards educational reforms in Nigeria which includes the inculcation of vocational education into the schools curriculum as a way of equipping students with practical skills and enhancing their employability.
A recent statement released by the National Orientation Agency (NOA), indicated that the government has added 15 vocational subjects to the Basic Education curriculum. These additions which take effect from January, 2025, they said, are designed to promote hands-on learning and better prepare students for the job market. The new subjects include: Plumbing, tiling and floor works, POP installation, Event decoration and management, Bakery and Confectionery, Hairstyling, Makeup, Interior Design, GSM Repairs, Satellite/TV Antenna Installation. Others are: CCTV and intercom installation and maintenance, solar installation and maintenance, garment making, agriculture and processing, which covers crop production, beekeeping, horticulture, and livestock farming (e.g., poultry and rabbit rearing) and Basic Digital Literacy, incorporating IT and robotics.
The former Minister of Education, Prof Tahir Mamman, who earlier hinted on the new curriculum for basic schools during a meeting with stakeholders in Abuja, last October, said under the new curriculum, pupils in basic schools will be required to acquire at least two skills. According to the former minister, “The idea is that by the time children finish school, they should have at least two skills. Students should be able to finish school with a minimum of two skills so that they can have a very productive life. “The basis for the curriculum is the National Skills Framework, and it has been approved. It’s a very big project; it affects all schools in Nigeria, public and private.“Whether in the public sector or private sector, all schools are going to implement it. So, this is already determined. It doesn’t require anybody’s consent or any institution can depart from it.
Speaking on implementation, the Mamman said, “We do not expect comprehensive, full implementation from January because, when you roll out something new, there’s a lot of preparation that has to take place by the schools, acquiring new things, equipment, and small things that they will need,” adding that plans were underway to ensure teachers were well-equipped for the new curriculum. He also spoke on the benefits of the curriculum, noting that it would rekindle the desire of parents and students to acquire formal education. Hear him, “Some parents do not want to send their children to school. Right now, part of the problem why schooling has become unattractive is because people finish and there’s no change in their lives. “They cannot be employed. They can’t do anything on their own. So, parents question the value of spending money to send their children to school. “Now it’s going to change that game altogether.
And we have seen how these things resonate with parents. When they are successfully implemented, you will see students will want to run to school every morning. Parents want to take their children to school because they are learning practical things while in school.”The Acting Executive Secretary of the Nigerian Educational Research and Development Council, Dr Margret Lawani, had also disclosed during the same event that the newly introduced subjects fell under the vocational and entrepreneurship studies framework, which has been designed to expose pupils to various trades across multiple sectors. In the views of some vocational training experts, the decision to include vocational education into the basic school curriculum is plausible as it comes at a time when the nation’s education system is facing mounting criticism for its inability to adequately prepare students for real-world challenges.
They opined that by introducing vocational training at an early age, Nigeria has an opportunity to bridge the gap between formal education and practical skill acquisition. They however noted that the success of this initiative hinges on thoughtful implementation and sustained support. “The problem of Nigeria has never been a dearth of ideas or policies on how to move the country forward. In the past some educationists came up with the idea of 6-3-3-4 system of education whereby Students would be taught introductory technology and other forms of vocational skills at the junior secondary school level to better equip them for the real world in future. What happened to that brilliant idea? How many schools have well-equipped laboratories and well-trained teachers to handle these technical and vocational subjects? “The idea of setting up technical schools and polytechnics across the country is for them to serve as a grooming ground for young Nigerians in the area of technology.
How has the government, both federal and states, supported these schools to succeed? So, our problem is lack of implementation, fragmented policies and lack of sustenance not lack of ideas”, posited one expert. He advised that for the new curriculum to bear positive fruits, the government must take time to sensitize heads and owners of schools, teachers, parents and pupils of both public and private schools on the importance of the subjects and assist the schools in acquiring the necessary equipment and tools for the smooth running of the curriculum. “These subjects being introduced cannot be taught only theoretically as we are used to in this country. They require regular practical classes which will cost some money. Government, via the ministries of education, must vote out money for these practical classes and be ready to supervise schools to ensure that they are doing the right thing,” he added
Noting the importance of vocational training in today’s Nigeria where the rate of unemployment is high, Mr. Abel Ikiriko, a basic technology teacher in a Private School at Trans Amadi, Port Harcourt, regretted that vocational training is often seen as a last resort for those who fail academically, leading to low enrolment. He said, “I say this because I am a teacher and I know what we see in school every day. When these vocational subjects are introduced, you will see parents who will go to their children’s schools to make trouble because the children are compelled to learn maybe Hairstyling or something like that. Every parent wants their children to be doctors, lawyers, engineers and other professions and never skilled persons because for our society, skilled jobs are for the dullards.” “One of the most pressing issues in our labor market is the skills gap. Employers often struggle to find workers with the right skills, despite high unemployment rates. Yet many youths are not willing to be trained in a vocation. They prefer to search for the unavailable white-collar jobs. So unfortunate,” he continued.
Ikiriko said that the inclusion of vocational training in primary schools has benefits that extend beyond future job prospects. “Hands-on activities help children develop critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity—skills that are essential in any field. Vocational subjects can also provide an alternative pathway for students who may not excel in traditional academic subjects, ensuring that no child is left behind in the education system. Moreover, these subjects can instill a sense of dignity in manual labor and shift societal perceptions about the value of skilled trades.”He advocated for public awareness campaigns so as to change perceptions about vocational education, and showcase its potential to lead to successful careers. Mrs. Meg Amadi, a mother of three pupils is concerned about the curriculum of the primary schools being overloaded, stressing that that is a potential risk.
According to her, primary school students are at a formative stage of their development, and overloading them with too many subjects could lead to cognitive fatigue. She maintained that careful planning is required to ensure that the new vocational subjects complement rather than compete with core academic learning; that they are seamlessly integrated into the broader curriculum without overwhelming students. To maximize the impact of this initiative, she offered the following suggestions: the government must invest in training and retraining teachers to deliver vocational subjects effectively, collaborating with vocational training institutes and NGOs for better result; government should begin with pilot programs in select schools to identify best practices and address challenges before scaling up nationwide; the private sector should be engaged to provide funding, equipment, and expertise for vocational training in schools.
Nonetheless, some analysts are of the view that the addition of 15 vocational subjects to the basic school curriculum is a visionary step toward transforming the nation’s education system and improving the nation’s economy. they hold that if implemented effectively, the initiative will equip young Nigerians with the skills needed to thrive in a rapidly changing world while fostering a culture of innovation and self-reliance. They said that with collaborative effort, strategic planning, and unwavering commitment from all stakeholders and the right execution, this bold move could serve as a model for other nations seeking to align education with the demands of the 21st century.
Calista Ezeaku
Features
Vocational Education And Nigeria’s Economy
The importance of vocational training to the development of any nation cannot be over emphasised. Technical education experts define vocational education as any form of educational program or course that focuses on teaching the specific skills and knowledge required for a particular job or trade. Unlike traditional academic education, which is often broader and theoretical, vocational training is practical, hands-on, and tailored to prepare individuals for specific careers or industries. They also argue that the dearth of trained vocational and middle-level technical manpower represents a very serious gap in the development of third-world countries, including Nigeria. This argument, perhaps, underscores the Federal Government’s bold move towards educational reforms in Nigeria which includes the inculcation of vocational education into the schools curriculum as a way of equipping students with practical skills and enhancing their employability.
A recent statement released by the National Orientation Agency (NOA), indicated that the government has added 15 vocational subjects to the Basic Education curriculum. These additions which take effect from January, 2025, they said, are designed to promote hands-on learning and better prepare students for the job market. The new subjects include: Plumbing, tiling and floor works, POP installation, Event decoration and management, Bakery and Confectionery, Hairstyling, Makeup, Interior Design, GSM Repairs, Satellite/TV Antenna Installation. Others are: CCTV and intercom installation and maintenance, solar installation and maintenance, garment making, agriculture and processing, which covers crop production, beekeeping, horticulture, and livestock farming (e.g., poultry and rabbit rearing) and Basic Digital Literacy, incorporating IT and robotics.
The former Minister of Education, Prof Tahir Mamman, who earlier hinted on the new curriculum for basic schools during a meeting with stakeholders in Abuja, last October, said under the new curriculum, pupils in basic schools will be required to acquire at least two skills. According to the former minister, “The idea is that by the time children finish school, they should have at least two skills. Students should be able to finish school with a minimum of two skills so that they can have a very productive life. “The basis for the curriculum is the National Skills Framework, and it has been approved. It’s a very big project; it affects all schools in Nigeria, public and private.“Whether in the public sector or private sector, all schools are going to implement it. So, this is already determined. It doesn’t require anybody’s consent or any institution can depart from it.
Speaking on implementation, the Mamman said, “We do not expect comprehensive, full implementation from January because, when you roll out something new, there’s a lot of preparation that has to take place by the schools, acquiring new things, equipment, and small things that they will need,” adding that plans were underway to ensure teachers were well-equipped for the new curriculum. He also spoke on the benefits of the curriculum, noting that it would rekindle the desire of parents and students to acquire formal education. Hear him, “Some parents do not want to send their children to school. Right now, part of the problem why schooling has become unattractive is because people finish and there’s no change in their lives. “They cannot be employed. They can’t do anything on their own. So, parents question the value of spending money to send their children to school. “Now it’s going to change that game altogether.
And we have seen how these things resonate with parents. When they are successfully implemented, you will see students will want to run to school every morning. Parents want to take their children to school because they are learning practical things while in school.”The Acting Executive Secretary of the Nigerian Educational Research and Development Council, Dr Margret Lawani, had also disclosed during the same event that the newly introduced subjects fell under the vocational and entrepreneurship studies framework, which has been designed to expose pupils to various trades across multiple sectors. In the views of some vocational training experts, the decision to include vocational education into the basic school curriculum is plausible as it comes at a time when the nation’s education system is facing mounting criticism for its inability to adequately prepare students for real-world challenges.
They opined that by introducing vocational training at an early age, Nigeria has an opportunity to bridge the gap between formal education and practical skill acquisition. They however noted that the success of this initiative hinges on thoughtful implementation and sustained support. “The problem of Nigeria has never been a dearth of ideas or policies on how to move the country forward. In the past some educationists came up with the idea of 6-3-3-4 system of education whereby Students would be taught introductory technology and other forms of vocational skills at the junior secondary school level to better equip them for the real world in future. What happened to that brilliant idea? How many schools have well-equipped laboratories and well-trained teachers to handle these technical and vocational subjects? “The idea of setting up technical schools and polytechnics across the country is for them to serve as a grooming ground for young Nigerians in the area of technology.
How has the government, both federal and states, supported these schools to succeed? So, our problem is lack of implementation, fragmented policies and lack of sustenance not lack of ideas”, posited one expert. He advised that for the new curriculum to bear positive fruits, the government must take time to sensitize heads and owners of schools, teachers, parents and pupils of both public and private schools on the importance of the subjects and assist the schools in acquiring the necessary equipment and tools for the smooth running of the curriculum. “These subjects being introduced cannot be taught only theoretically as we are used to in this country. They require regular practical classes which will cost some money. Government, via the ministries of education, must vote out money for these practical classes and be ready to supervise schools to ensure that they are doing the right thing,” he added
Noting the importance of vocational training in today’s Nigeria where the rate of unemployment is high, Mr. Abel Ikiriko, a basic technology teacher in a Private School at Trans Amadi, Port Harcourt, regretted that vocational training is often seen as a last resort for those who fail academically, leading to low enrolment. He said, “I say this because I am a teacher and I know what we see in school every day. When these vocational subjects are introduced, you will see parents who will go to their children’s schools to make trouble because the children are compelled to learn maybe Hairstyling or something like that. Every parent wants their children to be doctors, lawyers, engineers and other professions and never skilled persons because for our society, skilled jobs are for the dullards.” “One of the most pressing issues in our labor market is the skills gap. Employers often struggle to find workers with the right skills, despite high unemployment rates. Yet many youths are not willing to be trained in a vocation. They prefer to search for the unavailable white-collar jobs. So unfortunate,” he continued.
Ikiriko said that the inclusion of vocational training in primary schools has benefits that extend beyond future job prospects. “Hands-on activities help children develop critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity—skills that are essential in any field. Vocational subjects can also provide an alternative pathway for students who may not excel in traditional academic subjects, ensuring that no child is left behind in the education system. Moreover, these subjects can instill a sense of dignity in manual labor and shift societal perceptions about the value of skilled trades.”He advocated for public awareness campaigns so as to change perceptions about vocational education, and showcase its potential to lead to successful careers. Mrs. Meg Amadi, a mother of three pupils is concerned about the curriculum of the primary schools being overloaded, stressing that that is a potential risk.
According to her, primary school students are at a formative stage of their development, and overloading them with too many subjects could lead to cognitive fatigue. She maintained that careful planning is required to ensure that the new vocational subjects complement rather than compete with core academic learning; that they are seamlessly integrated into the broader curriculum without overwhelming students. To maximize the impact of this initiative, she offered the following suggestions: the government must invest in training and retraining teachers to deliver vocational subjects effectively, collaborating with vocational training institutes and NGOs for better result; government should begin with pilot programs in select schools to identify best practices and address challenges before scaling up nationwide; the private sector should be engaged to provide funding, equipment, and expertise for vocational training in schools.
Nonetheless, some analysts are of the view that the addition of 15 vocational subjects to the basic school curriculum is a visionary step toward transforming the nation’s education system and improving the nation’s economy. they hold that if implemented effectively, the initiative will equip young Nigerians with the skills needed to thrive in a rapidly changing world while fostering a culture of innovation and self-reliance. They said that with collaborative effort, strategic planning, and unwavering commitment from all stakeholders and the right execution, this bold move could serve as a model for other nations seeking to align education with the demands of the 21st century.
Calista Ezeaku
Features
A Farewell To Arms In Ogoni
For three decades or more, there has been a cessation of oil production activities in Ogoni land. But recent meeting of President Bola Tinubu with notable sons and groups may return Ogoni to renewed oil-production once again. Ogonis are weary of perennial neglect. Days after the meeting, President Tinubu gave a nod to the establishment of a University of Environmental Technology in Tai in the Ogoni area. He had earlier-on approved appointments into some federal boards in which some notable Ogonis were among the beneficiaries. The President’s actions and speeches so far have indicated good faith and good intentions. This has urged hard-nosed and irrepressible resistant leaders like Attorney Ledum Mitee, one-time President of the Movement for the Survival of Ogoni People (MOSOP), to be in complete agreement with the return to oil production.
He was heard on the news calling on all well- meaning sons and daughters of Ogoniland to accept the offers coming their way. Many Ogonis however, are still doubtful about the President’s intentions. They have said it is all geared towards the Federal Government having access to the rich oil and gas deposits in Ogoni soil. There is also distrust by some who have yet to heal from past injustices inflicted on the land by previous governments in cahoots with the oil majors. Since 1993 when oil production stopped in Ogoni land following intensive protests from the Ogoni people, the Nigerian government and the oil majors stopped reaping from millions of dollars in proceeds from the oil and gas. Lawson Hayford, a veteran journalist, who has reported the Niger Delta for over four decades, particularly the Niger Delta and the Ogoni crisis, said Nigeria has lost revenue amounting to over N30 trillion for the 32 years that oil has not been mined in Ogoni land.
Writing in the Southern Examiner, Hayford said, “While oil exploration and production in the Niger Delta region began in the late 1950s, operations were suspended in Ogoniland in the early 1990s due to disruptions from local public unrests with oil fields and installations remaining largely dormant for about 34 years, leading to a loss of revenue of over N30 trillion. “There are a total of 96 oil wells connected to five flow stations across the four local government areas of Khana, Gokana, Tai, and Eleme in Ogoniland. They were being operated by the Shell Petroleum Development Company, SPDC of Nigeria, a subsidiary of the Royal Dutch Shell.” That story is presently being rewritten by the remediation efforts of the Hydrocarbon Pollution Remediation Project (HYPREP) and the work of Prof Nenibarini Zabbey, its Project Coordinator.
“Over 50 communities are now enjoying potable water.” As though this was not magic enough, contractors are working hard toward mangrove regeneration not to leave out empowerment programmes for women and people with disabilities. These are stories too good to be true. In addition, the Petroleum Industry Act has also been introduced to take care of some basic needs of the oil communities, especially by tying development of the communities to the operational budgets of the oil companies. The establishment of a host community development trust as a condition for oil mining license holders regarding community development, may well be the magic wand required to turn things around for the Ogonis. A trying present is most likely to give way to a prosperous future. The future of the land and peoples of oil-bearing communities appear brighter with possibilities within this framework.
Environmentalist and lawyer, Iniro Wills, however, strongly thinks that the community-friendly clause in the PIA is only a tiny drop that cannot quench the thirst of the people’s appetite. Only time will tell. A lot of work needs to be done to bring every party in the Ogoni scenario to the table. Some groups are yet to agree with the return of oil production in Ogoniland, while others do not quite agree with the modus operandi adopted to initiate the process. They would all need to be brought together to ventilate their positions so that everyone is taken along together. Last Saturday, the committee that emerged to kickstart a process of the consultations initiated by President Tinubu convened a meeting at Freed Centre, Bori in the heart of Ogoniland. Though it was well attended, proceedings had to be hurried as a group of protesters stormed the venue.
Blessing Wikina, a long time public communications expert from Ogoni however, noted that the Bori meeting was a good landing. He said he was there. He dismissed the slanted reports about the meeting which he said were done to create social media content. He said in his social media handle that the committee deliberately avoided founding the consultations along old ‘loyalty blocs’ and ‘groups of people with entitlement blood.’ “Every Ogoni was to attend as an individual, not as a member of a camp. This approach meant no one would claim success or failure.”
Several factions exist in Ogoniland, including the leading pressure group, MOSOP, and they all need to get involved in the consultations, including those sulking for not being invited to the Abuja parley with the President.
Factional MOSO President, Fegalo Nsuke, recalled how MOSOP championed the Ogoni struggle from the beginning and wondered why MOSOP was not invited to Abuja or the Bori meeting. Hayford said, “sidelining MOSOP in the move to re-enter Ogoniland for oil and gas production could create distrust in the hearts of the Ogoni people, cautioning against rushing the process in order not to generate tension, anxiety and crisis in the landscape of Ogoni area.” Certain that the current process led by President Tinubu would yield good fruit for the Ogoni, Wikina says, he silently prays that “this oil resumption comes sooner, so that our people will participate in productive ventures around our oil economy…..and get benefits like our brothers in Orashi area, Bonny axis, etc.”
He cast a glance at the Bodo-Bonny road that will link mainland Nigeria with the vital island port of Bonny that is passing through Ogoniland. “Shall we wait, watch, as vehicles drive through here, to where lucrative oil businesses are happening…without our involvement? Every party will have to sheathe their sword and embrace the ongoing consultation process that will lead to a prosperous future for the land and the people.
Dagogo Josiah, Olayinka Coker and Emmanuel Obe
Josiah, Coker and Obe wrote in from Port Harcourt.

